Solar Panel
Categories
Solar Panel
Solar Power System
Solar Cell
Hot products
Your leading supplier of Baoding Dongliang New Energy Technology Co., Ltd
Baoding Dongliang New Energy Technology Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise focusing on the integrated application of photovoltaic products, committed to the design, research and development, production and sales of photovoltaic panels, solar power generation systems and other products.
Why Choose Us?
01/
Quality
We provide our customers with high-quality products, and we have applied for IEC, CE, ISO and other related certifications for our products.
02/
State-of-the-art equipment
We have 1 SMT production line, 2 photovoltaic production lines, 1 lithium battery pack line and other modern production lines.
03/
With 11 years of experience, we can develop, produce and sell any new energy-related products, modules, inverters, controllers, batteries, brackets, cables and other complete solutions according to your needs;
04/
The company has enough practice in the application of photovoltaic-related products, including grid-connected photovoltaic power generation, off-grid photovoltaic power generation, BIPV projects, wind-solar complementary projects, and application-oriented power supply systems (monitoring power supply, sensor power supply, solar street lights, etc.);

Polycrystalline Solar Panels
Read more
100 Watt Solar Panel
Read more
Black Monocrystalline Solar Panels
Read more
Eco 150w Solar Panel
Read more
Solar Panel 450 Watt Monocrystalline
Read more
450w Monocrystalline Solar Panel
Read more
Solar 450w Panel
Read more
Solar Panels
Read more
Solar Power Station
Read more
What is Solar Panel?
A solar panel is a device that converts sunlight into electricity by using photovoltaic (PV) cells. PV cells are made of materials that produce excited electrons when exposed to light. The electrons flow through a circuit and produce direct current (DC) electricity, which can be used to power various devices or be stored in batteries. Solar panels are also known as solar cell panels, solar electric panels, or PV modules.
Solar panels are usually arranged in groups called arrays or systems. A photovoltaic system consists of one or more solar panels, an inverter that converts DC electricity to alternating current (AC) electricity, and sometimes other components such as controllers, meters, and trackers. Most panels are in solar farms, which supply the electricity grid as can some rooftop solar.
Benefits Of Solar Panel
Cheaper electricity bills: Solar panels generate cost-free electricity, reducing overall energy costs.
Earn money back: Sell surplus energy to the grid for compensation through the Smart Export Guarantee (SEG).
Reduce carbon footprint: Sustainable energy reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
Year-round efficiency: Effective even in cloudy UK weather, especially with advancements in technology.
Low maintenance: Minimal upkeep required post-installation.
Independence from the grid: Generate your own electricity, reducing dependence on the grid.
Affordability: Solar panels are increasingly cost-effective.
Cost savings: Utilise solar energy to save money.
Grid independence: Keep your lights on during grid outages.
Increased home value: Installing solar energy can boost your property’s value.
Climate versatility: Solar systems work well in various climates.
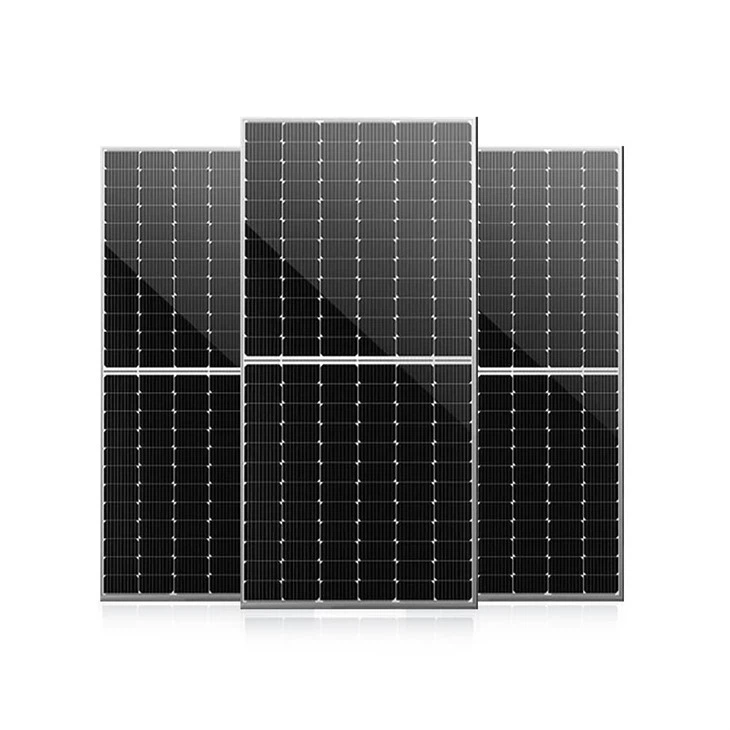

Application of Tier 1 Solar




Monocrystalline solar panels
Also known as single-crystal panels, these are made from a single pure silicon crystal that is cut into several wafers. Since they are made from pure silicon, they can be readily identified by their dark black color. The use of pure silicon also makes monocrystalline panels the most space-efficient and longest-lasting among all three solar panel types.
Polycrystalline solar panels
As the name implies, these come from different silicon crystals instead of one. The silicon fragments are melted and poured into a square mold. This makes polycrystalline cells much more affordable since there is hardly any wastage, and gives them that characteristic square shape.
Passivated emitter and rear cell (PERC) panels
PERC solar panels are an improvement of the traditional monocrystalline cell. This relatively new technology adds a passivation layer in the rear surface of the cell that enhances efficiency in several ways:
A: It reflects light back into the cell, increasing the amount of solar radiation that gets absorbed.
B: It reduces the natural tendency of electrons to recombine and inhibit the flow of electrons in the system.
C: It allows greater wavelengths of light to be reflected. Light waves over 1,180nm can’t be absorbed by silicon wafers and simply pass through, so they end up heating the cell’s metal back sheet and reduce its efficiency. The passivation layer reflects these higher wavelengths and stops them from heating up the back sheet.
Thin-film solar panels
Thin-film panels are characterized by very fine layers that are thin enough to be flexible. Each panel does not require a frame backing, making them lighter and easier to install. Unlike crystalline silicon panels that come in standardized sizes of 60, 72, and 96-cell counts, thin-film panels can come in different sizes to suit specific needs. However, they are less efficient than typical silicon solar panels.
Application of Solar Panel
Residential and commercial solar power systems: Solar cells are commonly used in residential and commercial buildings to generate electricity from sunlight. Solar panels, which consist of multiple solar cells, are installed on rooftops or in open areas to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. This electricity can be used to power homes, businesses, and other electrical devices, reducing the reliance on traditional grid electricity and lowering energy costs.
Remote power systems: Solar cells are ideal for powering remote locations that are not connected to the electrical grid. For example, solar panels can be used to provide electricity for off-grid cabins, remote telecommunication towers, weather stations, and other isolated installations. Solar power systems in these applications typically include batteries to store excess energy generated during the day for use at night or during periods of low sunlight.
Solar-powered vehicles: Solar cells can be integrated into vehicles to generate electricity for powering onboard systems or to supplement the vehicle’s main power source. Solar-powered cars, boats, drones, and even airplanes use solar cells to convert sunlight into electricity to drive electric motors or charge batteries. While solar power alone may not be sufficient to meet all the energy needs of a vehicle, it can help increase efficiency and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Components of Solar Panel
Solar cells
Solar cells are the building blocks of solar panels. Thousands of cells come together to form a solar panel. These Solar Cells are stringed together to make Solar Panels which involves soldering, encapsulating, mounting them on a metal frame, testing etc. The efficiency of a solar panel is directly proportionate to that of solar cells. The cost and efficiency of solar cells influence the overall performance of the solar panel. Solar Cell Efficiencies have improved continuously over the past decade.
Solar glass
Solar Glass is another important component of a solar panel. It is the outer most layer on the solar panel and has to be sturdy and shiny for better performance of the panel. The main function of solar glass is to protect the solar cells from harsh weather, dirt and dust. It is recommended to use tempered glass with 3mm – 4mmm thickness.
EVA
The EVA sheet or the ‘ethylene vinyl acetate’ is a highly transparent (plastic) layer used to encapsulate the cells. It provides laminated layering on top of the cells to hold them together. It should be durable as well as tolerant to withstand extreme temperatures and humidity.
Back sheet
Backsheet is the rear-most layer of the panel providing both mechanical protection and electrical insulation. It is essentially a protective layer.
Aluminum frame
The aluminum frame is also a crucial component as it provides structural strength to the panel. It is recommended to use a frame made of strong but lightweight material. It should be stiff and able to withstand extreme conditions like high wind and external forces. It generally comes in two makes – silver and anodised black.
Junction box
A junction box is fixed at the backside of the panel. It is the central point where cables interconnect with the panels.
Interconnector
Interconnectors help solar panels connect with one another. These should be extremely weather-resistant and should enable secure connections.
Silicon glue
Silicon is the most commonly used adhesive in a solar panel. Silicon creates strong bonds and is resistant to chemicals, moisture, and weather conditions. Hence silicon glue is used for solar panels. It is also the most common semiconductor material.
Process of Solar Panel
Building the solar cells
The primary components of a solar panel are its solar cells. P-type or n-type solar cells mix crystalline silicon, gallium, or boron to create silicon ingot. When phosphorus is added to the mix, the cells can conduct electricity. The silicon ingot is then cut into thin sheets and coated with an anti-reflective layer. Then, narrow slits are cut in the cells to funnel the flow of electricity.
Solder solar cells together to create a panel
After the phosphorus gives the silicon wafers their electrical charge, metal connectors link each solar cell in a process called soldering. The number of cells soldered together depends on how big the solar panel is manufactured. For reference, 60 cell-panels are standard size, and 72-cell panels are generally used for commercial projects.
Install a back sheet, front glass layer, and frame
A back sheet is installed to the bottom of the solar cells for protection, usually made from an ultra-durable plastic material. Next, a thin glass sheet is installed on top of the solar cells to filter the sunshine into the solar cells. These parts are held together by ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) glue. All these components are confined by a metal frame that latches onto mounting clamps on your roof.
Install the junction box
The junction box protects a solar panel’s wiring from damage to keep the flow of electricity moving from the panel to its inverter, preventing electricity from reversing direction. This functionality is essential when a solar panel isn’t producing electricity because that panel will try to consume energy instead. The junction box doesn’t allow any reversal of electric flow, so your solar panels can function correctly.
Quality testing
Each solar panel to hit the market is tested under Standard Test Conditions (STC) to ensure that the panels meet their projected outputs, efficiencies, and everything else the manufacturer promises in their technical specification sheet. Panels are put into a flash tester where “standard” conditions are simulated: 1000W/m2 irradiance, 25°C cell temperature, and an air mass of 1.5g. If it passes, the solar panel is ready for shipment and installation.
How to Maintain Solar Panel
Schedule regular cleaning
To keep solar panels in good condition, you must clean them at least twice a year: one at the end of fall and another at the start of winter. If they’re installed in an area with a high dust, pollen, or dirt concentration, it’s recommended to clean them more often, for example every three months.
Choose the right time
The maintenance and cleaning of solar panels must be carried out during the early hours of the morning, when the panels are fresher. Cleaning them when they are still warm or exposed to direct sunlight may be counterproductive, as the combination of heat and cold water can generate thermal stresses and damage the equipment. Avoid when windy, rainy, or snowy.
Schedule regular cleaning
If you haven’t detected any problems, you can start with the cleaning. Make sure you remove any kind of dirt, dust, or debris that may affect the performance of the solar panels.
Carry out a visual inspection
Before starting, carry out a visual inspection of the solar panels to identify possible damages such as cracks, breaks, or loose connections. If you detect any problems, contact a professional to carry out the necessary checks and repairs.
Dry the panels
You can let the solar panels air-dry, or you can use soft cloths. The most important thing is that no water residue remains that may affect the efficiency of the panels.
Monitoring
For proper maintenance, record the date you clean the solar panels, and schedule the next one. This will allow you to properly monitor and maintain the installation in optimal conditions.
What Are Solar Panels Made Out of?
Solar cells include a semiconducting material that converts sunlight into electricity by turning photons into electrons. Silicon is the most common material used as a semiconductor during the solar cell manufacturing process.
What are crystalline solar panels made out of?
Both monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels include silicon wafer cells. To build a crystalline panel, manufacturers assemble wafer cells into rows and columns to form a rectangle. They then cover the cells with a glass sheet and frame the glass.
Monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels vary in the composition of the silicon. Monocrystalline solar cells are cut from a single crystal of silicon. When manufacturers create polycrystalline solar cells, they melt fragments of silicon crystals together in a mold.
What are thin-film solar panels made out of?
Unlike monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels, thin-film panels can be made from multiple materials. The most prevalent type of thin-film solar panel is made from cadmium telluride (CdTe). To make this type of thin-film panel, manufacturers place a layer of CdTe between transparent conducting layers that help capture sunlight. This type of thin-film technology has a glass layer on the top for protection.
Thin-film solar panels can also use amorphous silicon (a-Si), similar to the composition of monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels. Though these thin-film panels use silicon layers in their composition, they are not made up of solid silicon wafers. Instead, they’re composed of non-crystalline silicon placed on top of glass, plastic, or metal.
Copper Indium Gallium Selenide (CIGS) panels are another popular type of thin-film technology. In CIGS panels, the semiconductor material made of copper, indium, gallium, and selenide, attaches to a conductive substrate made of glass, nylon, aluminum, or steel. Manufacturers place electrodes on the panels’ front and back to capture electrical currents.
How Shade Affects Solar Panel Efficiency
Shade has a greater impact on your solar panel’s performance than heat does.
Solar panels work in the shade, but it does reduce their output. As a general rule, solar panels produce about half as much energy under clouds and shade as they do under direct sunlight. However, solar technology is improving all the time. The solar panels we installed are designed to perform in all weather conditions and are ideal for the New England climate. Solar batteries can also help when it’s overcast by giving you access to stored solar energy when your panels are not producing enough power.
Shade may come from a number of sources besides clouds, including trees and roof components like chimneys and dormers. Keep in mind, however, that the shade on a roof tends to change throughout the day as the sun travels through the sky—your roof may still be a good candidate for solar even if it receives some shade throughout the day. We will assess your property before installing your solar panels to determine its solar potential and design a custom solar array that maximizes efficiency and output on your roof.
Our Factory
At present, the company has more than 200 employees, including 20 R & D technicians, and has more than 10,000 production workshops, 1 SMT production line, 3 photovoltaic production lines, 2 lithium battery pack line and other modern production lines. The annual production capacity of photovoltaic modules reaches 15 megawatts.





Our Certificate




FAQ
Q: What is a solar panel easy definition?
A: Solar panels are devices that convert light into electricity. They are called “solar” panels because most of the time, the most powerful source of light available is the Sun, called Sol by astronomers. Some scientists call them photovoltaics which means, basically, “light-electricity.”
Q: What exactly do solar panels do?
A: Solar power works by converting energy from the sun into power. There are two forms of energy generated from the sun for our use – electricity and heat. Both are generated through the use of solar panels, which range in size from residential rooftops to ‘solar farms’ stretching over acres of rural land.
Q: What is the purpose of the solar panel?
A: Solar panels, sometimes also called photovoltaics collect energy from the Sun in the form of sunlight and convert it into electricity that can be used to power homes or businesses. These panels can be used to supplement a building’s electricity or provide power at remote locations.
Q: What is a solar panel simple?
A: A solar panel is a device that converts sunlight into electricity by using photovoltaic (PV) cells. PV cells are made of materials that produce excited electrons when exposed to light.
Q: Is solar panels actually worth it?
A: According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, the average household uses around 893 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity per month. On average, a residential solar setup can produce between 350 kwh to 850 kWh per month. Therefore, going solar can help you save as much as 95% off your utility bill.
Q: How long do solar panels last?
A: Between 20 and 30 years
Manufacturers design solar panels to last for decades. According to the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA), solar panels last between 20 and 30 years. Some well-made panels may even last up to 40 years.
Q: What happens at night if you have solar panels?
A: At night your solar panels and inverter power down. The inverter isn’t running overnight because it doesn’t want to draw power. Instead it’ll wake back up when the sun shines in the morning. Your home and solar system are connected to the utility grid.
Q: What's inside a solar panel?
A: What’s in a solar panel? By weight, the typical crystalline silicon solar panel is made of about 76% glass, 10% plastic polymer, 8% aluminum, 5% silicon, 1% copper, and less than 0.1% silver and other metals, according to the Institute for Sustainable Futures.
Q: Can I install solar panels myself?
A: Although you can install solar panels yourself in theory, professional installation is recommended if you want a solar energy system that is capable of powering an entire home, or even a small business.
Q: How often do solar panels need to be cleaned?
A: Every six months
Well, it depends, but most experts agree that cleaning solar panels an average of every six months is reasonable. However, there are times when you may need to get your solar panels cleaned earlier or wait longer. If you live in an area of dusty farmlands or the dessert, you’ll need them cleaned more often.
Q: Do solar panels need to be cleaned?
A: Solar panels usually only need to be cleaned once or twice a year, or even less if it rains a lot where you live.
Q: Do solar panels work in winter?
A: Solar panels work through all four seasons of the year, come rain or shine, or even hail or in light snow. But solar panels do generally produce less energy in winter. That’s because the days are shorter, so there are fewer hours of daylight and the sun is lower in the sky, on average.
Q: Do solar panels work when raining?
A: Solar panels are able to run in the rain, in most cases, because they are designed to capture and convert light into electricity. They will continue to generate power even during rainy or cloudy weather but it could be at a reduced efficiency.
Q: What wears out in solar panels?
A: By nature of their exposure to the elements, solar panels degrade over time. Heavy rainfall, snowfall, ice, as well as high temperatures cause hardening of the crystalline silicon, frame corrosion, and cell contamination.
Q: Do solar panels have plugs?
A: Plug-in solar panels feature a microinverter affixed to their back and a cord to plug into an exterior wall.
Q: Why are solar panels so expensive?
A: The price of solar includes soft and hard costs, including design services, local permitting, panels, installation labor, components, and maintenance. Solar incentives and rebates such as the Residential Clean Energy Credit make solar less expensive.
Q: Is it OK to pressure wash solar panels?
A: While solar panels can endure heavy rainstorms and even the strongest weather conditions, it is best to avoid pressure washers since they may scratch and damage the photovoltaic cells. High water pressure directly on the panels can damage the seal around the frame allowing water to enter inside the panels.
Q: What temperature do solar panels stop working?
A: 40 To 185 degrees Fahrenheit
If you’re thinking of installing solar panels, it’s important to know the temperature range that they’ll work in. Solar panels generally have an operating temperature range of – 40 to 185 degrees Fahrenheit.
Q: Should I leave my solar panels on all the time?
A: It’s usually best to leave the solar panel going at all times; getting slightly hotter isn’t going to hurt it and it will always have an electrical load, anyway. If you’re not planning on using the solar panel for a long time then it might make sense.
Q: Do solar panels get hot?
A: Residential solar panels are generally tested at about 77°F and are rated to perform at peak efficiency between 59°F and 95°F. But solar panels can get much hotter than that, especially during the summer. Just how hot do solar panels get? In direct sunlight, they can reach temperatures of 150°F or higher.
As one of the most professional solar panel manufacturers in China, we’re featured by quality products and good service. Please rest assured to buy customized solar panel made in China here from our factory.



